Welcome to ELECTRICAL ENCYCLOPEDIA. In this article we will study about the Power Measurement using Two Wattmeter Method.
Wattmeter consists of two coils:
i) A low resistance coil (also called current coil), which is inserted in series with the line carrying current.
ii) A high resistance coil (also called pressure coil), which is connected across the two points whose potential difference is to be measured.
From figure we can see that,
Current through W1 = Ir
Potential difference across W1 = (V)rb = Vr - Vb
Power Read by W1 = Ir*(Vr - Vb)----------------------1
Current through W2 = Iy
Potential difference across W2 = (V)yb = Vy - Vb
Power Read by W2 = Iy*(Vy - Vb) ---------------------2
Total power = Power read by W1 + Power read by W2
From eq 1 & eq 2, we get
Total Power = Ir(Vr - Vb) + Iy(Vy - Vb)
Total Power = (Vr * Ir) - (Vb*Ir) + (Vy*Iy) - (Vb*Iy)
Total Power = (Vr * Ir) + (Vy * Iy) - Vb*(Ir + Iy)
We know that, Ir + Iy + Ib = 0 (By Kirchoff's Current law)
Ir + Iy = -Ib
So, Total Power = (Vr * Ir) + (Vy * Iy) + Vb*(Ib)
W1 + W2 = P1 + P2 + P3
"Hence, the sum of the two wattmeter reading gives us the total power in the 3-phase circuit."
Thanks for reading.
Keep Sharing & loving.
Wattmeter consists of two coils:
i) A low resistance coil (also called current coil), which is inserted in series with the line carrying current.
ii) A high resistance coil (also called pressure coil), which is connected across the two points whose potential difference is to be measured.
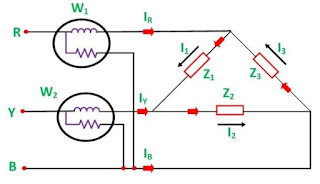
TWO WATTMETER METHOD
Circuit Arrangement for measuring power by two wattmeter method is shown in fig. below.
Current coils of the two wattmeter are inserted in any two lines and the potential coil of each wattmeter are joined to the third line.
According to Two wattmeter method, sum of the two wattmeter reading gives us the total power in the 3-phase circuit
Let W1 = Power measured by Wattmeter 1.
W2 = Power measured by Wattmeter 2.
P1 = Power Absorbed by load 1 (load on R-phase) = Vr*Ir.
P2 = Power Absored by load 2 (load on Y- phase) = Vy*Iy.
P3 = Power Absored by load 3 (load on B- phase). = Vb*Ib.
From figure we can see that,
Current through W1 = Ir
Potential difference across W1 = (V)rb = Vr - Vb
Power Read by W1 = Ir*(Vr - Vb)----------------------1
Current through W2 = Iy
Potential difference across W2 = (V)yb = Vy - Vb
Power Read by W2 = Iy*(Vy - Vb) ---------------------2
Total power = Power read by W1 + Power read by W2
From eq 1 & eq 2, we get
Total Power = Ir(Vr - Vb) + Iy(Vy - Vb)
Total Power = (Vr * Ir) - (Vb*Ir) + (Vy*Iy) - (Vb*Iy)
Total Power = (Vr * Ir) + (Vy * Iy) - Vb*(Ir + Iy)
We know that, Ir + Iy + Ib = 0 (By Kirchoff's Current law)
Ir + Iy = -Ib
So, Total Power = (Vr * Ir) + (Vy * Iy) + Vb*(Ib)
W1 + W2 = P1 + P2 + P3
"Hence, the sum of the two wattmeter reading gives us the total power in the 3-phase circuit."
Thanks for reading.
Keep Sharing & loving.