Welcome to ELECTRICAL ENCYCLOPEDIA. In this article, we will
study about the “Construction of Synchronous Machine”.
Unlike other electrical machines, In synchronous machine,
armature windings are placed on the stator and it has rotating field.
A Synchronous Machine consists of stator and rotor. Stator
is the stationary part of the machine and it carries the armature winding.
Output of the machine is taken from the stator.
Rotor is the rotating part of the machine. Field windings
are placed on the rotor and it produces the main field flux.
STATOR CONSTRUCTION
Various parts of the stator includes the frame, stator core,
stator windings and cooling arrangement. Frame may be of cast iron for
small-size machine and of welded steel for large-size machine. 3-phase winding also
called armature winding is placed in the slots cut on the inner periphery of the stator,
Stator core is assembled with thin sheets of high grade
silicon steel laminations.
Note that Armature Windings are placed in the Stator.
 |
| STATOR OF ALTERNATOR |
ROTOR CONSTRUCTION
There are two types of rotor construction namely, salient
pole type and cylindrical rotor type.
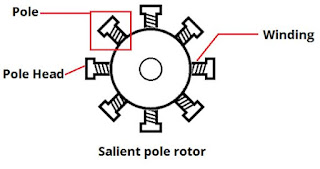
1. Salient-Pole Rotor
Term salient means ‘projecting’. Therefore, a salient pole
rotor consists of poles projecting out from the surface of the rotor core as
shown in the figure below.
As we can see from the figure, a salient-pole synchronous
machine has a non-uniform air gap. Air gap is minimum under the pole centres
and it is maximum in between the poles. The pole faces are so shaped that
radial air gap increases from the pole centre to the pole tips so that flux
distribution in the air gap is sinusoidal and it helps the machine to generate
sinusoidal emf.
Since the rotor is subjected to changing magnetic fields,
therefore it is made up of thin steel laminations to reduce eddy current loss.
Salient-pole rotor have concentrated windings on the pole.
Ends of the field winding are connected to the dc source through brushes on the
slip rings. DC source may be a dc generator which provides excitation to the
field windings.
Salient Pole Rotor has larger diameter and short axial
length as well as they operate at lower speeds. They have vertical configuration
installation.
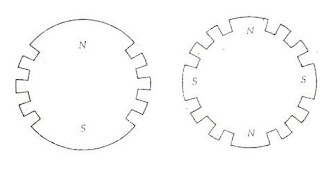
2. Cylindrical Rotor
Also called non-salient pole type rotor. Rotor is so
constructed that it forms a smooth cylinder and no physical poles are seen as
in salient pole type rotor.
 |
| CYLINDRICAL ROTOR |
As shown in the above figure, two-third of the rotor
periphery, slots are cut at regular intervals and parallel to the shaft. DC
field windings are placed in these slots. Windings are of distributed type.
They have comparatively small diameter and long axial length. Because of
uniform air gap, its operation is less noisy and less windage losses.
Cylindrical Rotors are particularly used in high-speed
machines. They have horizontal configuration installation.
Thanks for reading.
Keep Sharing & Loving.