Swinburne's test is an indirect method of testing DC machines (either motor or generator), especially shunt and compound machines where the value of flux almost remains constant.
Figure shown below shows the arrangement for Swinburne's Test on DC Machine.
First of all ,machine whose efficiency is to be determined is operated at no load and Constant Loss of that machine is determined.
Let, V = Supply Voltage
Iₒ = No-load Current
Iₛₕ = Shunt field Current
Iₐₒ = Iₒ - Iₛₕ = No-load armature Current
Rₐ = Armature Resistance
Note that the Shunt Field Current remains same irrespective of the load.
No-load Input Power = V×Iₒ ..........eq 1
We know that when DC Machine is at no-load, then its input power is used only to supply losses and losses at no-load are:
So, No-load Armature Copper losses = Iₐₒ²× Rₐ = (Iₒ - Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ .........eq 2
Since, No-Load Input Power = No-load Armature Copper losses + Constant Losses;
Constant Losses = No-Load Input Power - No-load Armature Copper losses
So putting the values from eq1 & eq2 , we get
Since we have determined the Constant loss of the machine, now efficiency of the machine can be found at any other load.
Input Power to Motor = V×I
Armature Current in case of motoring operation = Iₐ = Iₒ - Iₛₕ
Armature Copper loss = Iₐ²×Rₐ = (I - Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ
Total Loss in the Motor = Armature Copper loss + Constant Loss
Total Loss in the Motor = {(I - Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ} + Pc
Motor Efficiency = {Input - loss}/Input
Motor Efficiency,
{(V×I) - [(I - Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ] + Pc} / V×I
Input Power to Generator = V×I
Armature Current in case of generating operation = Iₐ = I + Iₛₕ
Armature Copper loss = Iₐ²×Rₐ = (I + Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ
Total Loss in the Generator = Armature Copper loss + Constant Loss
Total Loss in the Generator = {(I + Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ} + Pc
Generator Efficiency = Output/{Output + loss}
Generator Efficiency,
(V×I )/{(V×I) + [(I + Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ] + Pc}
2. Since the constant loss is already determined, so efficiency at any load can be found.
Thanks for reading.
Keep sharing and loving.
Figure shown below shows the arrangement for Swinburne's Test on DC Machine.
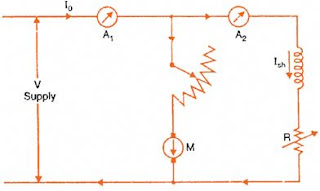 |
| SWINBURNE TEST OF DC MACHINE |
First of all ,machine whose efficiency is to be determined is operated at no load and Constant Loss of that machine is determined.
Let, V = Supply Voltage
Iₒ = No-load Current
Iₛₕ = Shunt field Current
Iₐₒ = Iₒ - Iₛₕ = No-load armature Current
Rₐ = Armature Resistance
Note that the Shunt Field Current remains same irrespective of the load.
No-load Input Power = V×Iₒ ..........eq 1
We know that when DC Machine is at no-load, then its input power is used only to supply losses and losses at no-load are:
So, No-load Armature Copper losses = Iₐₒ²× Rₐ = (Iₒ - Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ .........eq 2
Since, No-Load Input Power = No-load Armature Copper losses + Constant Losses;
Constant Losses = No-Load Input Power - No-load Armature Copper losses
So putting the values from eq1 & eq2 , we get
Constant Loss,
Pc = (V×Iₒ) - (Iₒ - Iₛₕ)² × RₐSince we have determined the Constant loss of the machine, now efficiency of the machine can be found at any other load.
EFFICIENCY WHEN RUNNING AS MOTOR
Let I = Load Current at which efficiency is to be found.Input Power to Motor = V×I
Armature Current in case of motoring operation = Iₐ = Iₒ - Iₛₕ
Armature Copper loss = Iₐ²×Rₐ = (I - Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ
Total Loss in the Motor = Armature Copper loss + Constant Loss
Total Loss in the Motor = {(I - Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ} + Pc
Motor Efficiency = {Input - loss}/Input
Motor Efficiency,
{(V×I) - [(I - Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ] + Pc} / V×I
EFFICIENCY WHEN RUNNING AS GENERATOR
Let I = Load Current at which efficiency is to be found.Input Power to Generator = V×I
Armature Current in case of generating operation = Iₐ = I + Iₛₕ
Armature Copper loss = Iₐ²×Rₐ = (I + Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ
Total Loss in the Generator = Armature Copper loss + Constant Loss
Total Loss in the Generator = {(I + Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ} + Pc
Generator Efficiency = Output/{Output + loss}
Generator Efficiency,
(V×I )/{(V×I) + [(I + Iₛₕ)² × Rₐ] + Pc}
ADVANTAGES OF SWINBURNE'S TEST
1. Power Required for carrying out this test is small, therefore this method is an economical and convenient method of testing DC Machines.2. Since the constant loss is already determined, so efficiency at any load can be found.
DISADVANTAGES OF SWINBURNE'S TEST
1. Variation in the iron loss from full load to no-load is not considered during calculation. Due to armature reaction, iron loss is increased at full load.
2. As the Swinburne's test is performed at no-load so, temperature rise and commutation at full load is not considered while calculation in constant loss.LIMITATION OF SWINBURNE'S TEST
Swinburne's test is only applicable for the machines having constant flux like shunt and compound. Swinburne test is not suitable for DC Series machine.Thanks for reading.
Keep sharing and loving.